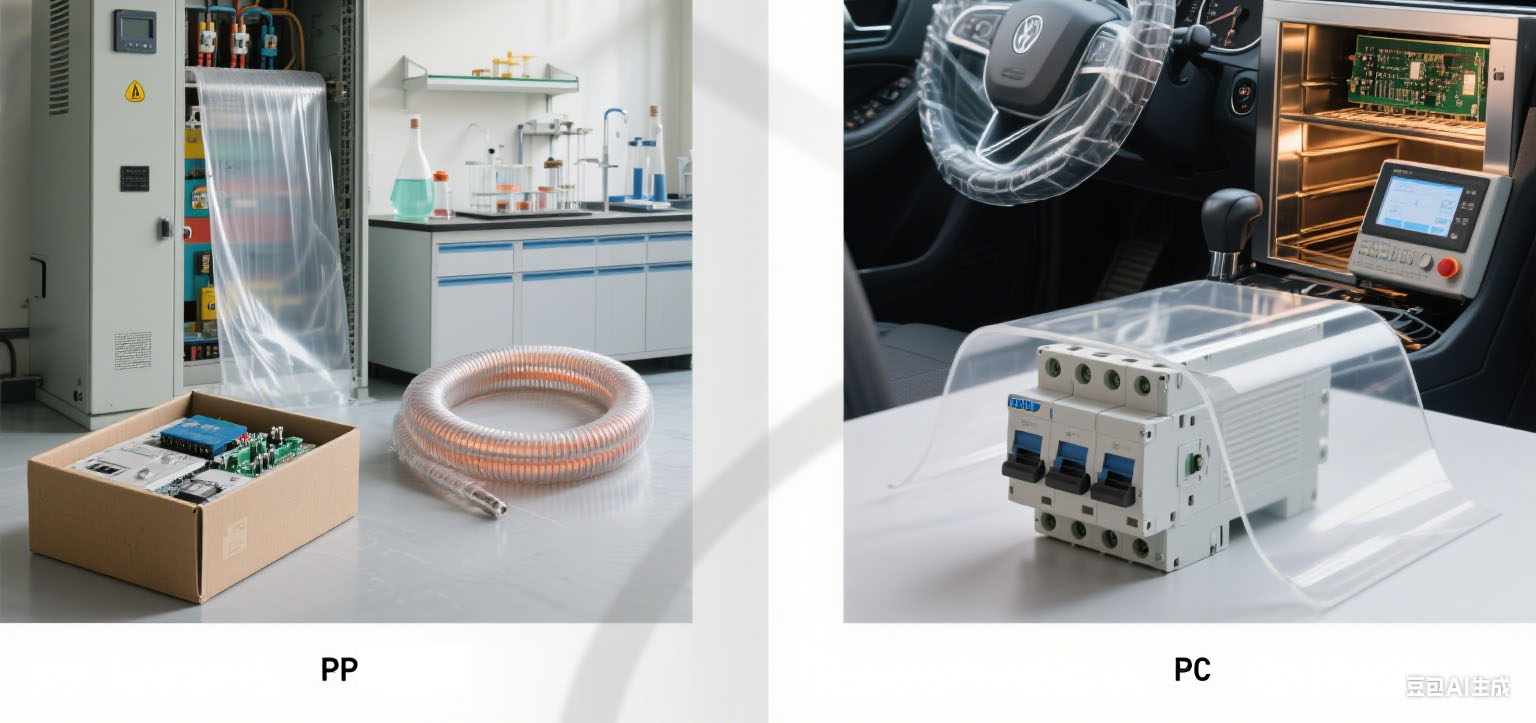
Polypropylene (PP) and polycarbonate (PC) membranes serve distinct roles in insulation, each suited to specific needs based on their properties.
PP membranes thrive in scenarios leveraging their unique traits:
- High-frequency electrical systems: Their low dielectric constant (2.2-2.4) minimizes energy loss, ideal for telecom gear and radio frequency devices.
- Chemical environments: Resistant to solvents, acids, and bases, they’re used in pharmaceutical processing, agricultural irrigation insulation, and food machinery.
- Flexible needs: They conform to irregular surfaces, fitting applications like flexible heaters.
- Low-cost projects: Practical for consumer electronics packaging, offering affordable basic insulation.
PC Membrane Applications in Insulation
PC membranes excel in demanding conditions:
- High-impact settings: Protect automotive dashboard electronics and industrial machinery from vibrations and impacts.
- High temperatures: Withstand 120-130°C, suitable for near-engine parts, industrial ovens, and heat-generating lighting.
- Optical needs: Their clarity works for display devices and control panels requiring visibility through insulation.
- Rigid structures: Provide insulation and support in electrical enclosures, resisting external pressure.
In short, PP and PC membranes meet diverse insulation needs, with their applications tied to their distinct properties.